Rotator Cuff Injury
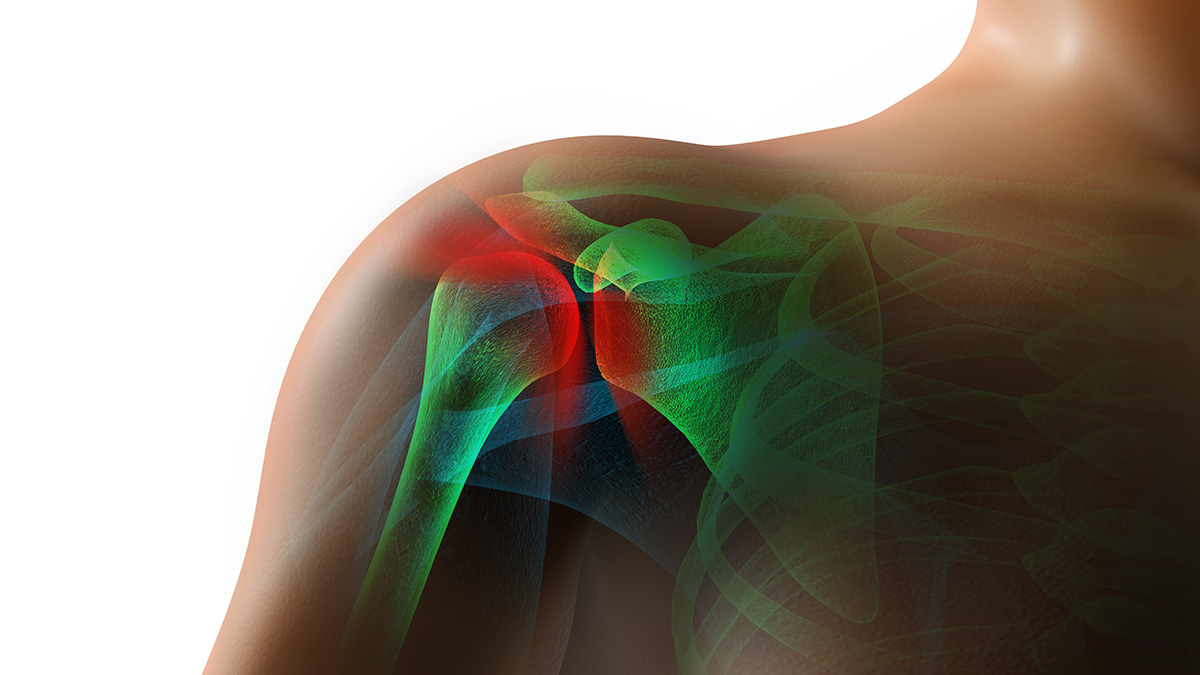
Your rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint, keeping the head of your upper arm bone firmly within the shallow socket of your shoulder. A rotator cuff injury can cause a dull ache in the shoulder, which often worsens with the use of your arm.
Rotator cuff injuries are common and increase with age. These may occur earlier in people who have jobs that require repeatedly performing overhead motions. Many people with a rotator cuff injury can manage their symptoms and return to activities with physical therapy exercises that improve flexibility and strength of the muscles surrounding the shoulder joint.
Sometimes, a rotator cuff tear/strain/sprain may occur as a result of a single injury. In those circumstances, medical evaluation should be provided as soon as possible to discuss the role of surgery.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of a rotator cuff injury are:
- Dull ache deep within the shoulder
- Arm weakness
- Difficulty lifting or using your arm
- Disturbed sleep
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Conservative treatments, such as rest, ice, and physical therapy, are sometimes all that’s needed to recover from a rotator cuff injury. Other treatments include:
Injections
When conservative treatments haven’t reduced your pain, a steroid injection into your shoulder joint may be recommended, especially if the pain is interfering with your sleep, daily activities, or physical therapy.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is usually one of the first treatments recommended. Exercises tailored to the specific location of your rotator cuff injury can help restore flexibility and strength to your shoulder. Physical therapy is also an important part of the recovery process after rotator cuff surgery.