Thyroid and Parathyroid Gland Tumors
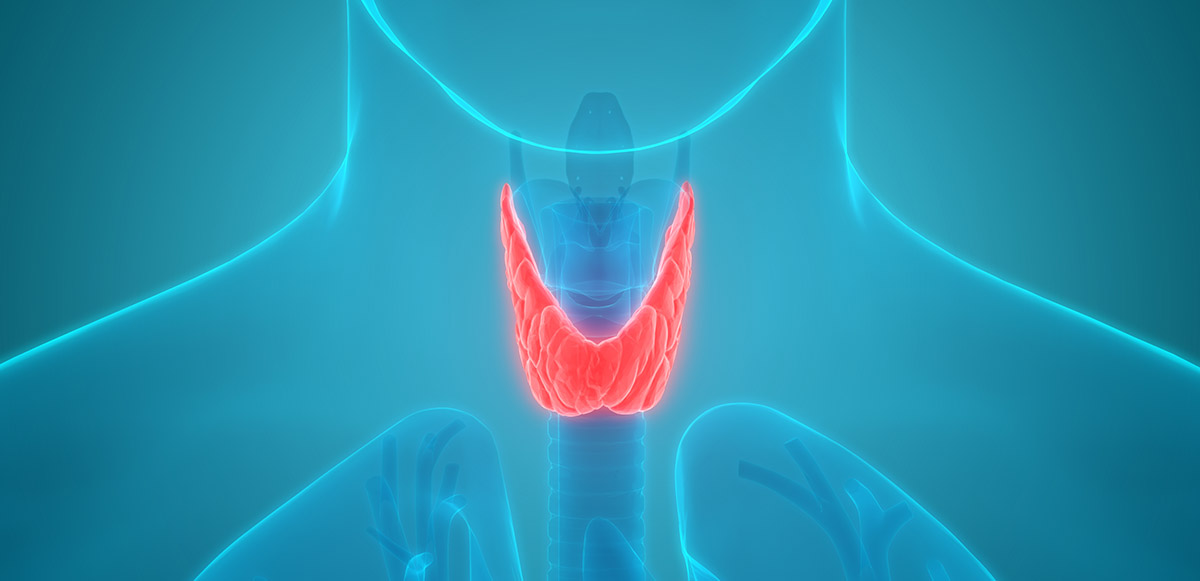
The thyroid gland is located in the front of the neck at the base of the throat. Thyroid tumors are either benign or malignant growths. Examples of benign tumors are adenomas, which may secrete thyroid hormone.
Thyroid adenomas are small growths (nodules) that start in the cell layer that lines the inner surface of the thyroid gland. The adenoma itself may secrete thyroid hormone. If the adenoma secretes enough thyroid hormone, it may cause hyperthyroidism.
Thyroid adenomas may be treated if they cause hyperthyroidism. Treatment may include surgery to remove part of the overactive nodule and/or medication.
Parathyroid Tumors
There are four parathyroid glands, which are located in your neck or upper chest near the thyroid gland.
Most parathyroid tumors are benign and the most common cause is hyperparathyroidism, which leads to increased blood calcium levels.
There is a rare cancer that sometimes forms in tissues of one or more parathyroid glands. That cancer can be treated with surgery or radiation therapy.
Symptoms
Symptoms of thyroid and parathyroid tumors may include:
- Hoarseness or loss of voice
- Difficulty swallowing
- Throat or neck pain that doesn’t go away
- Persistent cough
- Breathing problems
Treatment
Benign thyroid tumors (adenomas) may be treated if they cause hyperthyroidism. Treatment may include surgery to remove part of the overactive nodule and/or medication.
If cancer is present, it will typically be treated with surgery to remove the thyroid gland and sometimes nearby lymph nodes. Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and/or targeted drugs may also be recommended.