Pituitary Tumors
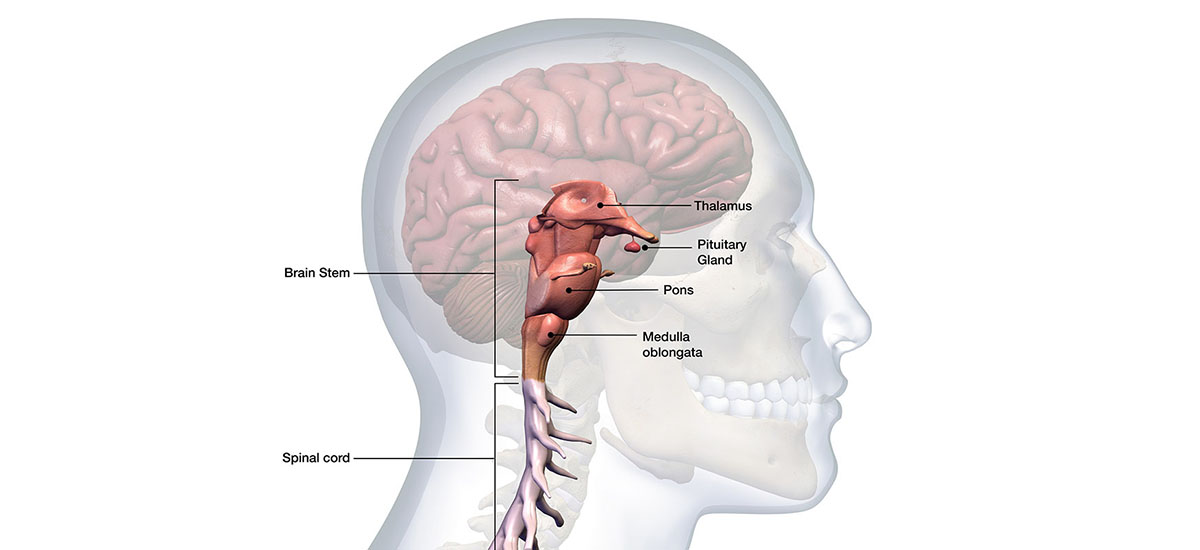
A pituitary tumor is an abnormal growth in the pituitary gland, which is located at the base of the brain. Often called the “master gland” of the body, the pituitary is part of the endocrine system and helps control the release of hormones from other endocrine glands, such as the thyroid, sex glands (testes or ovaries), and adrenal glands. The pituitary also releases hormones that directly affect body tissues, such as bones and breast milk glands.
As many as 20 percent of the population have pituitary tumors, most of which are benign (noncancerous). Many of these tumors don’t cause symptoms so are never diagnosed during the person’s lifetime. However, as a pituitary tumor grows, its hormone-releasing cells may be damaged and no longer release the correct amount of hormones.
Symptoms
Symptoms can include:
- Trouble with vision
- Headache
- Endocrine abnormalities (confirmed by their primary care physician and a referral to the endocrinologist)
Treatment
Most pituitary tumors should be removed through surgery, especially if the tumor is pressing on an optic nerve. The majority of pituitary tumors can be surgically removed through the nasal cavity with the assistance of an endoscope and without an incision. At BSSNY, both the Neurosurgeon and Head & Neck Surgeon work together to remove the tumor.