Stroke symptoms
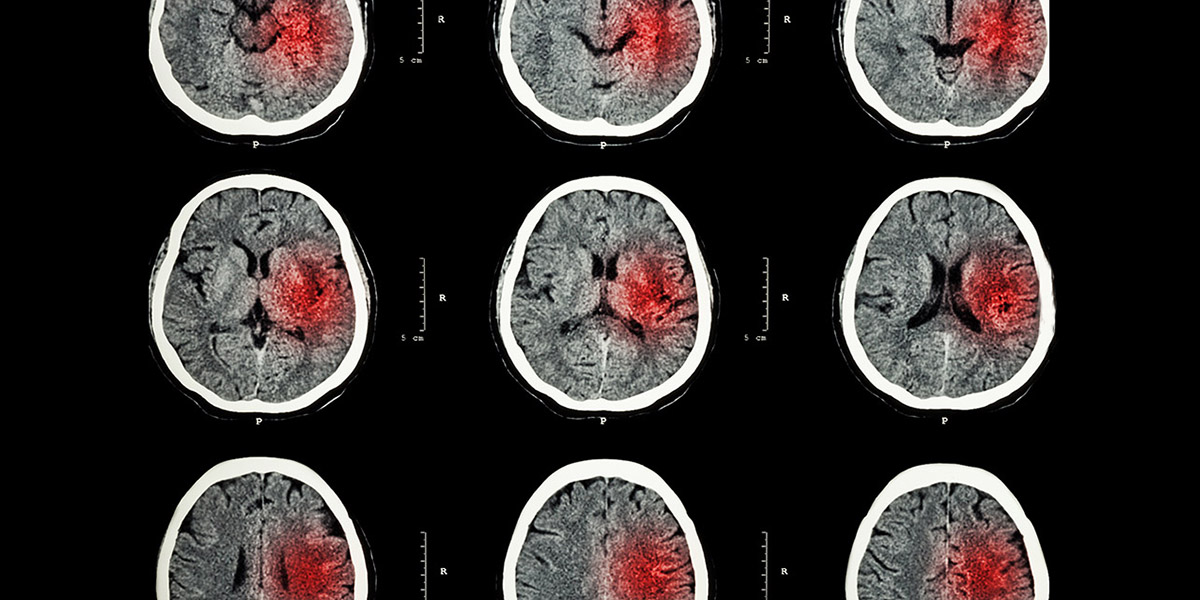
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of your brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients. Brain cells begin to die in minutes.
Most strokes are caused by an abrupt blockage of arteries leading to the brain (called schematic stroke). Other strokes are caused by bleeding into brain tissue when a blood vessel bursts (called hemorrhagic stroke). Because strokes appear rapidly and require immediate treatment, a stroke is also called a brain attack. When the symptoms of a stroke last only a short time (less than an hour), this is called a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or mini-stroke.
A stroke is a medical emergency, and prompt treatment is crucial. Early action can reduce brain damage and other complications.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a stroke can include:
- Trouble speaking or slurring your words
- Understanding what others are saying and general confusion
- Paralysis or numbness of the face, arm, or leg
- Vision problems
- Sudden, severe headache
- Vomiting, dizziness, or altered consciousness
- Trouble walking or loss of balance
Treatment
Early treatment with medications like tPA (clot buster) can minimize brain damage. Other treatments focus on limiting complications and preventing additional strokes.
If you’ve had a stroke or symptoms and an artery is up to 50 percent blocked, surgery may help you.